I’m currently learning DevOps Beginners to Advanced with Projects on Udemy. Here are some notes on using AWS.
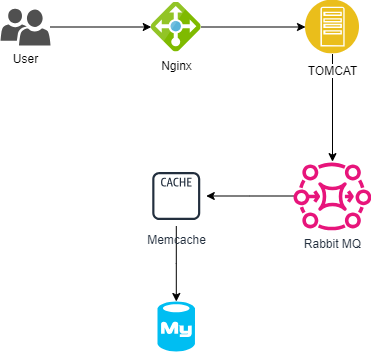
Original Application Stack
- Nginx
- Apache
- Tomcat
- RabbitMQ
- Memcache
- Mysql
Migration Goals
- EC2
- VMs for tomcat, rabbitmq, memcache, mysql
- ELB (Elastic Load Balancer)
- Replaces nginx for load balancing
- Autoscaling
- Automation for VM scaling
- S3/EFS
- Shared storage
- Route 53
- Private DNS service
Target Architecture
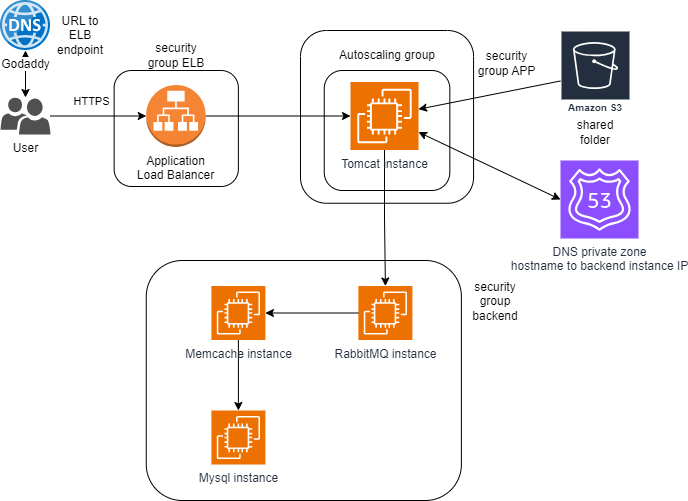
Flow of Execution
- Create key pairs
- Create security groups
- Split into three groups:
- LB (replaces nginx)
- APP (for tomcat)
- Backend (including rabbitmq, memcache, mysql)
- Split into three groups:
- Launch instances with user data
- Currently a semi-automated process
- Manually create instances and paste shell scripts for environment setup into userdata
- Update IP to name mapping in Route 53
- Set up an internal DNS for communication between instances using hostnames
- Build the application from source code
- This part is still semi-automated. Build the Java project on the local machine.
- Upload to S3 bucket
- Use AWS CLI to upload the built Java WAR file to the APP instance.
- Download artifact to Tomcat EC2 instance
- Previously, we used keys for S3 access. Here, instances connect to S3 using IAM roles.
- Create a new S3 access role in IAM.
- Attach the created role to the APP instance.
- Use aws s3 ls to confirm successful access.
- Previously, we used keys for S3 access. Here, instances connect to S3 using IAM roles.
- Set up ELB with HTTPS (certificate from Amazon Certificate Manager)
- Create a target group, ensuring it points to port 8080 on the app.
- Create an ELB with HTTP/HTTPS routing to the target group.
- Purchase a domain and apply for an SSL certificate from AWS Certificate Manager.
- In the secure listener, select the SSL certificate from ACM.
- Map ELB endpoint to website name in DNS
- At the DNS provider (in this case, GoDaddy), create a CNAME record that redirects to the AWS LB domain.
- Verify
- DNS settings may take some time to propagate.
- You can directly access the LB’s domain to check if the APP is running on port 80.
- Build an autoscaling group for the tomcat instance
- Autoscaling involves three steps:
- AMI (Amazon Machine Image)
- Create an image from the current APP instance.
- Launch template
- Use the created AMI, and keep the security group the same as the original APP.
- Autoscaling group
- Attach it to the existing load balancer.
- Choose the load balancer’s target group.
- Set scaling policies based on CPU usage or network in/out.
- Configure notifications.
- AMI (Amazon Machine Image)
- Autoscaling involves three steps: